¶ UV Ceti
¶ 历史背景
通常也叫flare star。flare可能存在于非常宽的波长范围,从射电到x-ray波段,时间从几分钟到几个小时不等。
耀发时V波段星等可增加6个星等。
大多数都是年轻的低质量红矮星。
光谱型大多为F-M,在M星中会更常见。
大质量的RS CVn也会有flare。
虽然flare star可能早在1924年就被探测到,但最早被证实的观测是W.J. Luyten在V1396 Cyg和AT Mic中发现了强烈的可变光谱。
1999年Gershberg, R. E.等人整理了之前文章中发现的UV Ceti变星约463个[1],2014年Tamazian, V. S.等人整理了一百余例双星UV Ceti变星。
¶ 物理图像
¶ 在赫罗图上的位置
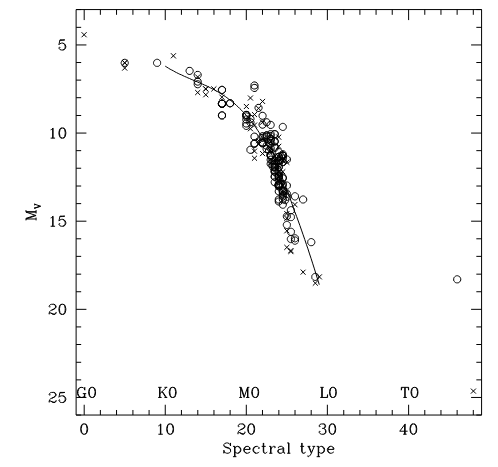
图1.UV Ceti bianry variables的光谱型[2]
¶ 基本信息
-大部分仍处于主序前阶段,处于T Tauri之前的演化阶段[3],耀发活动在高光度时更强,并随着年龄的增长而减弱[4]。
-通常光谱中可检测到H和Ga II发射线,表明有色球层活动。
-变化特征是恒星亮度快速、不规则、大幅度增加,随后是一个非常缓慢的衰减(从几分钟到几小时),回到静止水平。最强烈的变化发生在光谱的蓝色端:一次耀斑可能会导致v波段亮度变化1等,但在u波段亮度变化5等。耀发通常伴随着恒星的发射谱线变亮,特别是巴尔默系列氢的发射谱线,以及电离氦谱线的出现。在无线电和x射线光谱区域也观测到了耀发,但不一定与光学耀发同时发生。
-耀发在几乎所有方面都类似于太阳耀发
¶ 典型天体
¶ 天体基本信息
1.UV Ceti,1948年首次看到UV Ceti的flare[5]。
2.Proxima Centauri
3.Wolf 359
4.Barnard's Star(BY Dra & UV Ceti)
5.TVLM513-46546
¶ 光变曲线

图2.Proxima Centauri的光变曲线
¶ 耀发图像
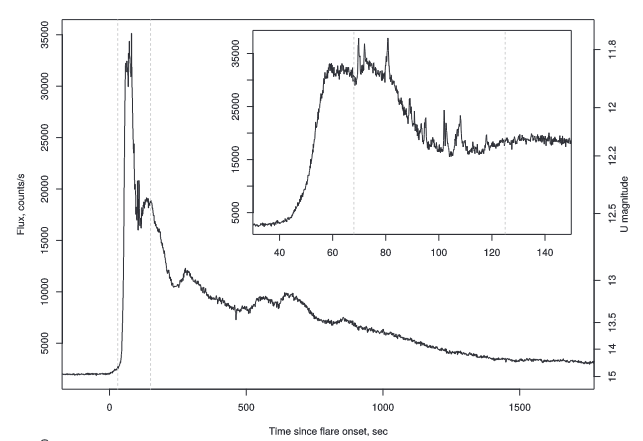
图3.UV Ceti在2008.12.28的一次耀发图像[6]
¶ 重要文献
2020年-至今关于UV Ceti的文章(https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/user/libraries/xG647WNcT3uTBL_a77wS5w)
¶ 参考文献
Gershberg, R. E., Katsova, M. M., Lovkaya, M. N., Terebizh, A. V., and Shakhovskaya, N. I., “Catalogue and bibliography of the UV Cet-type flare stars and related objects in the solar vicinity”, Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series, vol. 139, pp. 555–558, 1999. doi:10.1051/aas:1999407. ↩︎
Tamazian, V. S. and Malkov, O. Y., “Catalog of Binary UV Ceti Type Flare Stars”, Acta Astronomica, vol. 64, no. 4, pp. 359–369, 2014. ↩︎
Mirzoyan, L. V., “On the origin of the UV Ceti type stars.”, in Physics and Evolution of Stars: Star Clusters and Associations, 1990, no. 6, pp. 51–53. ↩︎
Mirzoyan, L. V. and Hambarian, V. V., “Subsystems of Flare Stars of Different Ages in Orion and the Pleiades”, Astrophysics, vol. 37, p. 36, 1994. doi:10.1007/BF02113993. ↩︎
Joy, A. H. and Humason, M. L., “Observations of the Faint Dwarf Star L 726-8”, Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, vol. 61, no. 360, pp. 133–134, 1949. doi:10.1086/126150. ↩︎
Beskin, G., Karpov, S., Plokhotnichenko, V., Stepanov, A., and Tsap, Y., “Polarimetric Observations of Flare Stars”, in Stars: From Collapse to Collapse, 2017, vol. 510, p. 303. ↩︎